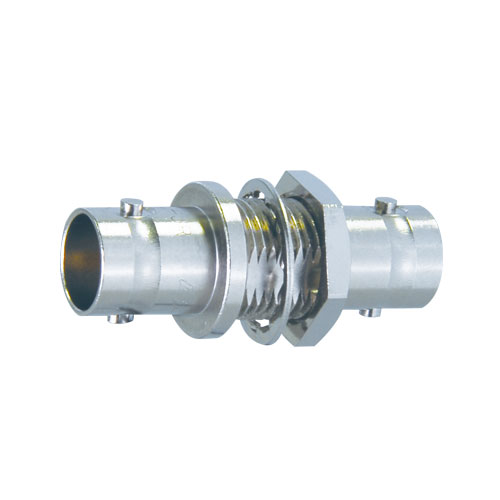
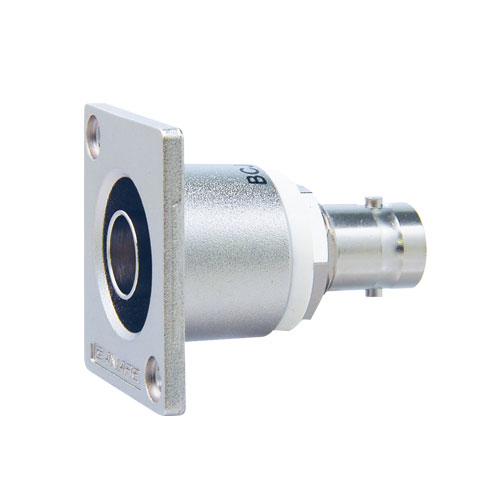
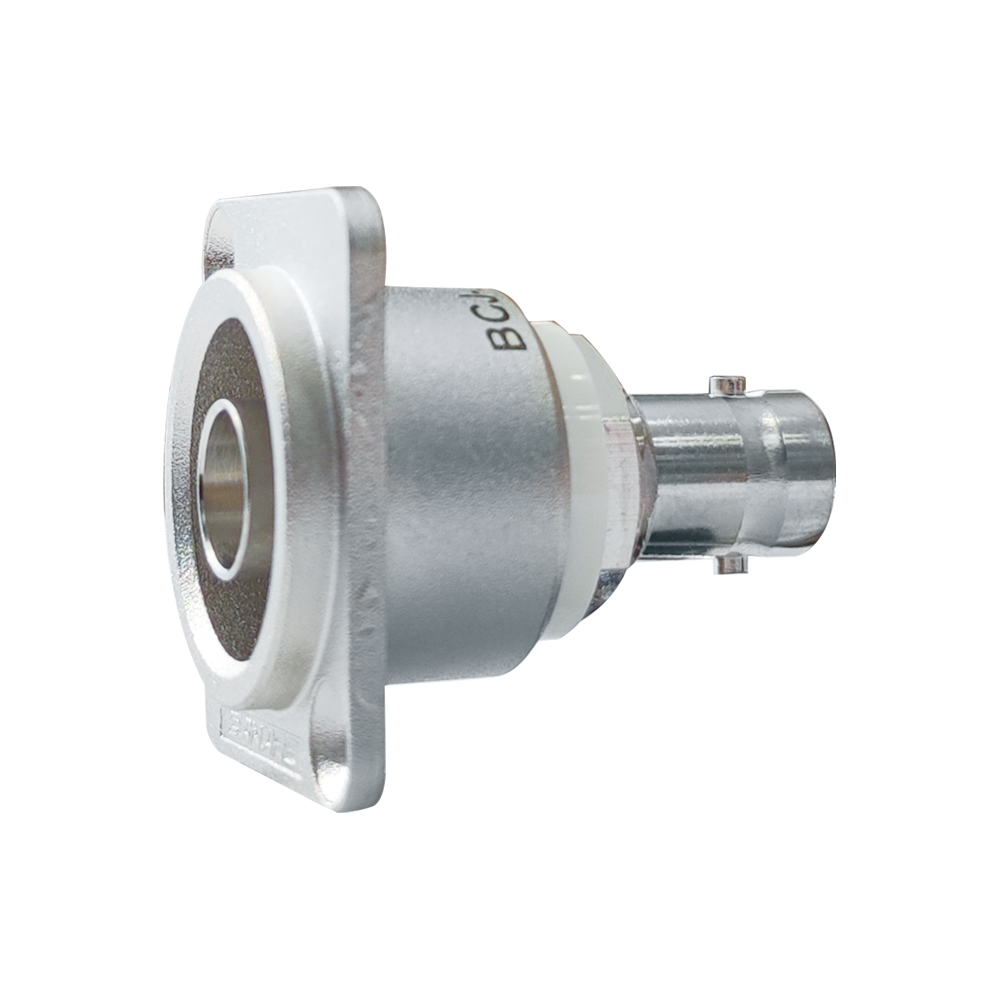
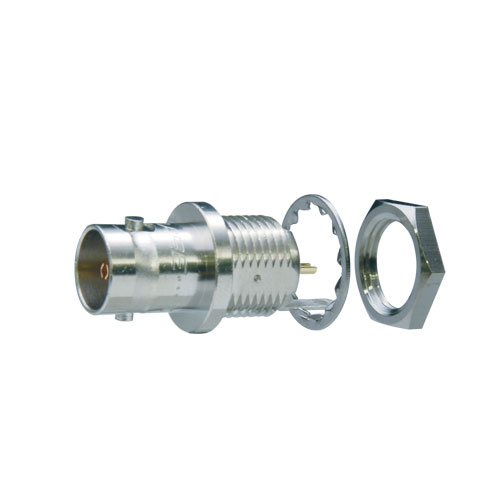
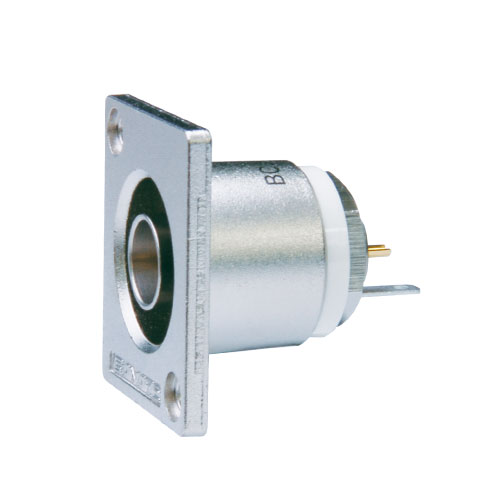
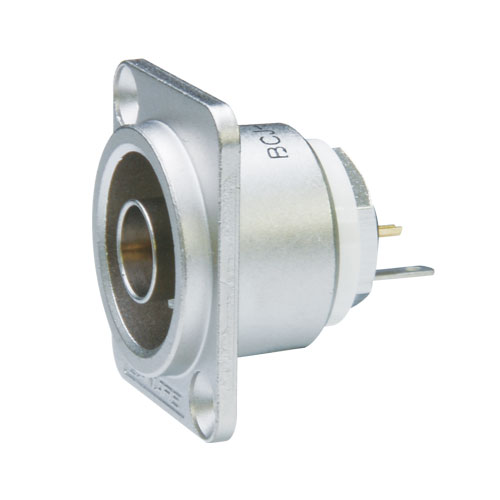
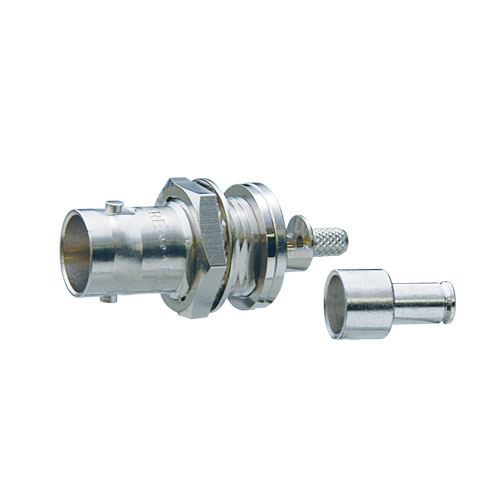
75 ohm BNC Receptacles
True 75 ohm impedance.
Key Features and Benefits
- Gold plated beryllium copper center contact.
- Flush-mount receptacle prevents damage on the jack.
- Tech Data
- Tech Note
- Downloads
Jack to Jack12G SDI
| Model | Description | Flange | Standard package |
|---|---|---|---|
| BCJ-JRK | Standoff | - | 20 pcs |
| BCJ-JRUK | Flush-mount | ITT XLR-F77 | |
| BCJ-JRUDK | Neutrik D | ||
| BCJ-JRUDBK | Neutrik D (Black) |
Key Features and Benefits
- Redesigned for 12G-SDI to minimize return loss.
- Return Loss: 26.4 dB @ 12 GHz, 15 dB @ 12 GHz
Jack to Jack
| Model | Description | Flange | Standard package |
|---|---|---|---|
| BCJ-JRUD | Flush-mount | Neutrik D | 20 pcs |
Key Features and Benefits
- Return Loss: 26.4 dB @ 2 GHz
Jack to Solder
| Model | Description | Flange | Standard package |
|---|---|---|---|
| BCJ-R | Rear-mount | - | 20 pcs |
| BCJ-R/1 | Rear-mount, w/Ground Lug | - | |
| BCJ-RU | Flush-mount | ITT XLR-F77 | |
| BCJ-RUD | Neutrik D | ||
| BCJ-RUDB | Neutrik D (Black) |
Key Features and Benefits
- Panel Jack covers the rear wiring part with metal crimp sleeve.
- Return Loss: 26.4 dB @ 2 GHz
Panel Jack (Jack to Solder and Crimp)
| Model | Description | Flange | Suitable Cable | Die Set | Standard package |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BCJ-FC1 | Front-mount, 1/2" | - | 1.5C-2V | TCD-1DB | 20 pcs |
| BCJ-FC1-7/16 | Front-mount, 7/16 | - | |||
| BCJ-RUC1 | Flush-mount | ITT XLR-F77 |
Key Features and Benefits
- Panel Jack covers the rear wiring part with metal crimp sleeve.
- Space-saving design
- Ideal for internal rack wiring.
- Return Loss: 26.4 dB @ 1 GHz
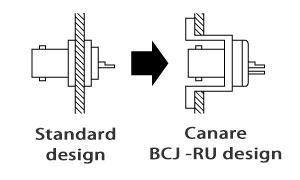
- Note1: Be sure to use Canare Crimp Tool
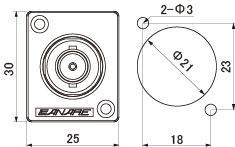
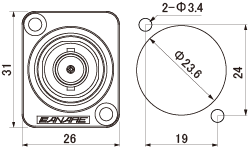
< Panel Hole Dimensions >
| BCJ-RUC1 , BCJ-RU , BCJ-JRUK | BCJ-RUD , BCJ-RUDB , BCJ-JRUD(K) , BCJ-JRUDBK |
|---|---|
 |
 |
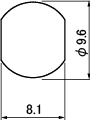
| BCJ-R | *BCJ-R/1 , *BCJ-JRK | BCJ-FC1 | *BCJ-FC1-7/16 |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
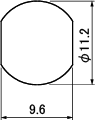 |
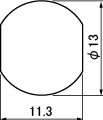 |
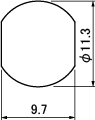 |
- * marked models accept insulation bushing IU-7/16, and the panel hole for IU-7/16 should be adopted in this case.
Technical Note
Voltage Standing - wave Ratio (VSWR) and Return Loss
Terminating the receiving end of a limited length coaxial cable using a resistance value not equal to its characteristic impedance creates a reflected wave that returns back down the cable to the sending end. The result is interference developing between the travelling wave and the return wave which results in a standing wave that causes voltage levels to fluctuate. The degree to which terminating resistance matches the characteristic impedance is indicated using the VSWR or voltage standing-wave ratio standard shown in Fig. 1. Going hand in hand with the VSWR ratio is the return loss factor which measures the size of the reflected wave current in relation to the travelling wave current. (See Fig. 2)
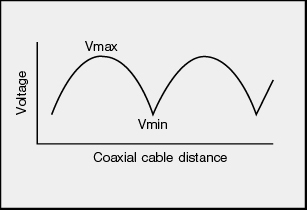
Fig. 1 Voltage Distribution Over Coaxial Cable
| VSWR | Return Loss (dB) |
|---|---|
| 2 | 9.54 |
| 1.5 | 13.98 |
| 1.2 | 20.83 |
| 1.1 | 26.44 |
| 1.05 | 32.26 |
| 1.02 | 40.09 |
| 1.01 | 46.06 |
Fig. 2 VSWR to Return Loss Conversion Table







